Renaissance and Reformation
1. The difference between the Renaissance in Italy and the Renaissance in Spain was ____.
a) Spain was inspired by Greco-Roman culture and Italy was inspired by early Christain writers
b) Spain was inspired by early Christain writers and Italy was inspired by Greco-Roman culture
c) Spain was inspired by early Christain writers and Italy was inspired by Confusian writings
d) Spain was inspired by Greco-Roman culture and Italy was inspired by early Buddist writers
2. Which was the most important invention of the Renaissance?
a) wheel b) automobile c) printing press d) can opener
3. The philosophy concerned, not with religious matters, but with everyday human problems is ___.
a) humanism b) humanitarianism c) humanology d) human instinct
4. Utopia means ____.
a) belief in many goods b) perfect society c) military government d) game boards
5. _____ was a scientist of the Renaissance through using a telescope discovered new things about our solar system. He was later excommunicated from the church for his findings.
a) More b) Dante c) Medici d) Galileo
6.A major goal of the Counter-Reformation was to
(a) reinstate the power of the Roman Catholic Church
(b) reduce the authority of absolute monarchs
(c) encourage new ideas in science and philosophy throughout Europe
(d) compromise with European Protestants
7. Which of the following was not a philosopher during the Renaissance?
a) Erasmus b) Aristotle c) Thomas More d) Mirandola
8. Spanish writer of the book Don Quixote who pointed humor at feudalism was ____.
a) Machiavelli b) Cervantes c) Michelangelo d) Shakespeare
9. Italian who painted the Sistine Chapel was _____.
a) Machiavelli b) Cervantes c) Michelangelo d) Shakespeare
10. One way in which the writers of the Renaissance were influenced by the writers of ancient Greece was that the Renaissance writers
a) stressed the power of human reason
b) promoted the religious doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church
c) showed little interest in secular affairs
d) produced few new scientific ideas
11. The Renaissance is said to be ____.
a) transition of the Roman Empire to the Middle Ages
b) transition of the Middle Ages to modern times
c) transition of Catholic Europe to Muslim Europe
d) movement to destroy Greco-Roman culture
12. The Renaissance occurred in the ____.
a) 1st century B.C. b) 6th Century A.D. c) 8th Century A.D. d) 15th century A.D.
1. The Renaissance began in Italy because Italy
(a) was a united nation with a strong central government
(b) had annexed territory in the eastern Mediterranean
(c) was close to Muslim writers from Africa
(d) was a source for Greco-Roman culture.
2. Two early centers of European Renaissance culture were
(a) London and Prague (b) Madrid and Berlin c) Paris and Athens (d) Venice and Florence.
3. The Medicis and Sforzas played a significant part in the Renaissance as
(a) painters of everyday scenes
(b) business people of Italian cities and patrons of culture
(c) scientists who furthered medical research
(d) serfs whose conquests spread the Renaissance to northern Europe.
4. The Mona Lisa was painted by ___
a) Michelangelo b) Raphael c) da Vinci d) Feinman
5. The Protestant Reformation was
(a) delayed by the questioning attitude engendered by the Renaissance
(b) a complete surprise to Catholic leaders
(c) supported by many rulers who desired Church properties
(d) hastened by the election of an Englishman the Hall of Science.
6. Nepotism meant
(a) filling Church positions with relatives
(b) filling Church positions by means of competitive examinations
(c) failing to live the spiritual and humble life required of Church officials
(d) selling Church positions. for money
19. The Lollards were followers of ____.
a) John Huss b) John Wycliffe c) John Johnson d) John Pencils
20. The _____ was a period during which the popes lived at Avignon, France, under the domination of French kings
a)Great Schism b) Babylonian Captivity c) Great Escape d) French Acquisition
21. Sect means a(n) ___.
a) military tactic b) farm tool c) idea d) group
22. During the early Middle Ages, western European societies were most influenced by
(a) national monarchies
(b) the Roman Catholic Church
(c) elected parliaments
(d) the Byzantine emperors
23. In western Europe, a long-term effect of the invention of Gutenberg’s printing press was that the ___.
(a) Reformation ceased to progress
(b) feudal system declined
(c) literacy rate increased
(d) development of new ideas was discouraged
24. Simony meant
(a) filling Church positions with relatives
(b) filling Church positions by means of competitive examinations
(c) failing to live the spiritual and humble life required of Church officials
(d) selling Church positions. for money
• Sale of indulgences authorized by Pope Leo X to raise money to build St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome (1515)
• Ninety-five Theses posted (1517)
• Selling indulgences on the streets of Wittenburg (1517)
25. These events are most closely associated with
(a) Hamurabi and absolutism
(b) Martin Luther and the Protestant Reformation
(c) Pericles and the Golden Age of Greece
(d) Leonardo daVinci and scientific socialism
26. _____ is a form of Protestantism.
a) Humanisticism b) Islam c) Lutheranism d) Judaism
27. The Church of England is called the ___ faith.
a) Puritan b) German c) Yorkshire d) Anglican
28. The theory of _____ by John Calvin said that only those elected beforehand by God would achieve salvation.
a) animism b) predestination c) excommunication d) religioisization
29. One of the results of the Black Death in Europe was ____.
a) people left for America to escape the disease
b) working people gained more social and economic power
c) the population of Italy increased
d) the Catholic Church gained economic and political power
30. Secular means ___.
(a) use of alchemy and magic
(b) the literature of Greece and Rome
(c) non-religious
(d) following the teachings of Mohammed.
A reason for Luther's protest against the Catholic Church was
a)simony b) the sale of indulgences c) the papal refusal to pray d) German invasions
1. The Renaissance in western Europe was a period marked by
(a) unquestioned reliance on the teachings of Confucius
(b) an advance of Moslem culture
(c) Christian unity throughout all of North America
(d) a rebirth of culture in Europe.
2. An important feature of the Renaissance was an emphasis on
(a) alchemy and magic
(b) the literature of Greece and Rome
(c) chivalry
(d) the teachings of St. Thomas Aquinas.
3. Secular means ___.
(a) use of alchemy and magic
(b) the literature of Greece and Rome
(c) chivalry in religious matters
(d) following the teachings of Mohammed.
4. One of the results of the Black Death in Europe was ____.
a) people left for America to escape the disease
b) working people gained more social and economic power
c) the population of Italy increased
d) the Catholic Church gained economic and political power
5. Another name for the Black Death was the ___.
a) bubonic plague b) Renaissance c) boil plague d) Greco-Roman lego
1. One way in which the writers of the Renaissance were influenced by the writers of ancient Greece was that the Renaissance writers
a) stressed the power of human reason
b) promoted the religious doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church
c) showed little interest in secular affairs
d) produced few new scientific ideas
2. The Renaissance is said to be ____.
a) transition of the Roman Empire to the Middle Ages
b) transition of the Middle Ages to modern times
c) transition of Catholic Europe to Muslim Europe
d) movement to destroy Greco-Roman culture
3. The bubonic plague changed the economic relationship between the upper and lower classes of Europe. This occurred because ___
a) jobs were plentiful and peasants and craftspeople were in scarce supply
b) there were fewer jobs because of the population decline
c) nobles paid less because they needed less
d) nobles raised wages because the plague was a warning sign from God.
4. Another name for the bubonic plague was ____.
a) Black Death b) Renaissance c) boil plague d) Greco-Roman lego
5. The Renaissance occurred in the ____.
a) 1st century B.C. b) 6th Century A.D. c) 8th Century A.D. d) 15th century A.D.
1. Two great Italian cities of trade were _____
a) Rome and Florence b) Venice and Genoa c) Ravenna and Genoa d) Nasti and Florence
2. Lorenzo the Magnificent was from which great Italian family?
a) Medici b) Sforza c) Piazza d) daVinci
3. The reason many Greeks from the Byzantine empire settled in Italy was because __.
a) it was close to Greece
b) the Turks forced them to settle there
c) Italy had a large Muslim population
d) Oxford and Harvard universities were in Itlay
4. Which great Italian family lived in Milan?
a) Medici b) Sforza c) Piazza d) daVinci
5. The largest kingdom or city-state on the Italian peninsula was ____.
a) Florence b) Milan c) Kingdom of the Two Sicilies d) daVinci
Extra Credit
Please answer the document based questions below on your answer sheet. This is extra credit but you must do it if you have time. If you are wrong no points will be taken off your exam. You will get extra points on this exam if you answer the questions correctly.
“We are free and can now worship and live in the way that we want. No longer are we subject to the constraints put on us from the foreign leader in Rome. Since I am an Englishman, I can pray in English not in the dead Latin language. Because I can pray and worship according to my ways, I feel a closer bond with my spiritual nature. “
John Greystoke, Arthronshire, 1588.
The quote means:
How does this relate to the Reformation?
Middle Ages in Europe , Middle East in the Middle Ages
1. The first Bishop of Rome, from whose office evolved the papacy, was
a) Paul b). Peter c) Patrick d) Augustine.
2. Which of the following is not a position in the Roman Catholic hierarchy?
a) cardinal b) bishop c) tribune d) pope
3. _____ ended the persecution of Christians in Rome.
a) Conquest of Constantine
b) Conquest of Mohammed
c) Eastern Orthodox split
d) Theodosius Mandate
4. All Muslims must make a pilgrimage to _____ once in their lifetime.
a) Medina b) Mecca c) Jerusalem d) Constantinople
5. The Muslim religion is ____.
a) polytheistic
b) somewhat based on Jewish and Christian writings
c) a major influence on the Jewish faith.
d) based on Chinese star charts
6. The Christian faith is based on the teachings of _____.
a) Julius Caesar b) Mohammed c) Jesus of Nazareth d) Buddha
7. _____ is the missionary responsible for converting the Irish to Christianity.
a) Paul b). Peter c) Patrick d) Augustine.
8. One of the economic activities the Roman Catholic Church did in the Middle Ages was ____.
a) build bridges across the English Channel
b) establish schools and hospitals
c) build great arenas for sporting events
d) create the steam engine
9. The holy book of the Muslim faith is ____.
a) the Bible b) Hammurabi’s Code c) the Koran d) the Hegira
10. Which European country did the Moslems conquer and occupy for close to 800 years?
a) England b) France c) Spain d) Germany
11. A basic reason for the rise of the feudal system in Europe was the
a. increase in population
b. influence of the Crusades
c. end of the manorial system
d. lack of effective central governments.
12. A group originating from Scandinavia that attacked Western Europe from 800 to 1000 A.D. were the __
a) Moors b) Moops c) Vikings d) Magyars
13. The lowest class in feudal society was the ____.
a) king b) knight c) clergy d) serf
14. The only way to emerge from your social class in the early Middle Ages was to be a(n) __.
a) serf b) clergy c) lawyer d) farmer
15. Which of the following governments had the most power in the early Western European Middle Ages?
a) central b) manor c) state d) national
16. Which barbarian group settled in Hungary?
a) Moors b) Retrents c) Vikings d) Magyars
17. The Frankish leader who defeated the Moors at the Battle of Tours was
a) Clovis b) Charlemagne c) Pepin d) Charles Martel.
18. Charlemagne was able to dominate western Europe successfully because he
a) controlled the commerce of this area
b) allied himself with Anglo-Saxon England
c) maintained an efficient military force
d) developed Frankish sea power.
19. Areas that Charlemagne united within his empire are now part of
a) France and Germany
b) England and Spain
c) Spain and Portugal
d) Austria and Russia.
20. A result of Charlemagne's conquests was the
a) spread of Christianity
b) union of the Eastern and Western Roman empires
c) expulsion of the Moslems from Europe
d) decline of capitalism in central Europe.
21. The "Dark Ages" in western Europe refers to the period
a) before the dawn of history
b) soon after the assassination of Julius Caesar
c) following the collapse of the Roman Empire
d) directly following the end of the Pax Romana.
22. _____ was the name of the Germanic barbarian group that conquered and settled in England during the early Dark Ages.
a) Franks b) Goths c) Anglo-Saxons d) Moslems
23. Why did learning and culture decline in the Dark Ages?
a) roads were destroyed
b) schools and libraries were destroyed
c) no large armies to carry books
d) people spoke Arabic
24. What country or area in Europe continued recording historical events during the Dark Ages?
a) Poland b) England c) Ireland d) Arabia
25. The Middle Ages took place approximately from ______.
a) 1000B.C. to 500 B.C.
b) 500 B.C. to 500 A.D.
c) 500 A.D. to 1300 A.D.
d) 1300 A.D. to 1965 A.D.
Geoffrey Chaucer wrote _____.
a) Divine Comedy b) Canterbury Tales c) Chanson de Geste d) Legeric
The purpose of the medieval guilds was to ____.
a) abolish the use of goods from the Middle East
b) provide assistance to guild members
c) decrease learning in towns and cities
d) restore the manor system in Western Europe
An example of Gothic architecture is _____.
a) U.S. Capital building b) St. Patrick’s cathedral c) Leaning tower of Pisa
An apprentice is a(n) _____.
a) beginning worker b) monk c) intermediate worker d)shop owner
Local languages are known as the ______.
a) chanson de geste b) guilds c) local language d) method of building churches
1) The type of architecture in the Middle Ages that included rounded arches, a dome and columns is called _____ architecture
a) Gothic b) Romanesque c) chanson de geste d) jouneyman
2) Chanson de geste is a(n) ___.
a) type of architecture b) guild member c) form of money d) epic hero
3) Medieval craft guilds
a) encouraged competition
b) wanted to restore feudalism
c) established an apprentice system to train craftspeople
d) limited their activities to the production of goods.
4. Which of the following is not a reason for the expansion of culture in the Later Middle Ages?
a) the Catholic Church provided leadership and support,
b) the Crusades spread knowledge of the advanced Byzantine and Moslem civilizations,
c) the towns provided centers of culture and learning.
d) the increase in Viking invasions
5. Dante wrote ___
a) Divine Comedy b) Canterbury Tales c) Chanson de Geste d) Legeric
Which situation is the cause of the other three
a) development of a European bourgeoisie
b) increase in European demand for Middle Eastern goods
c) European renewal of interest in learning
d) European involvement in the Crusades
Which of the following was an important trading center in Italy during the later Middle Ages?
a) Rome b) Brussels c) Venice d) Hamburg
The German trading alliance started in the later Middle Ages was called the ____.
a) Hanseatic League b) German Trading Federation c) Die Trunmost
The _____ river was a an important trading highway during the later Middle Ages.
a) Thames b) Tiber c) Mississippi d) Rhine
5) The rise in lending money led to the establishment of ___.
a) navies b) armies c) banks d) department stores
1) The Hanseatic League was established to ___.
a) capture the Holy Land from the Turks
b) send trade expeditions to the Far East
c) halt the Moslem invasion of western Europe
d) protect trade and commerce in North European seas.
2) Bruges and Ghent, the famous medieval trade centers, are located in
a) Italy b) Germany c) England d) Belgium.
3)The growth of trade in medieval Europe resulted in
a) invasions by German barbarians
b) the decline of banking
c) an increase in the power of the nobles
d) the rise of a middle class.
4) The name of the middle class in the Later Middle Ages was ____.
a) patricians b) bourgeoisie c) maximas d) hanseatic
5) One result of the Crusades was an increase in trade between the Middle East and ___.
a) East Asia b) North America c) Africa d) Europe
1. A group originating from North Africa that attacked Western Europe from 800 to 1000 A.D. were the __
a) Moors b) Moops c) Vikings Magyars
2. Which group settled in Hungary?
a) Moors b) Moops c) Vikings Magyars
3. The highest class in feudal society was the ____.
a) king b) knight c) clergy d) serf
4. John of Boldland gets land from Lord John of Pencils in exchange for a military alliance. Andrew is a(n) _____.
a) serf b) upper (powerful) lord c) lesser lord d) feudalistic archaic
5. Which of the following governments had the most power in the early Western European Middle Ages?
a) central b) local c) state d) national
Essay
List the four pillars of Islam
Age of Absolutism, Miscellaneous questions
2 In the partial outline below, which heading belongs after Roman numeral I?
I. ________________________________
A. Louis XIV
B. Phillip II
C. Henry VIII
(1) Divine Right Monarchs
(2) Supporters of Democracy
(3) Religious Reformers
(4) Leaders of the Crusades
3 In western Europe, a long-term effect of the invention of Gutenberg’s printing press was that the
(1) monarchies were restored to absolute power
(2) feudal system declined
(3) literacy rate increased
(4) development of new ideas was discouraged
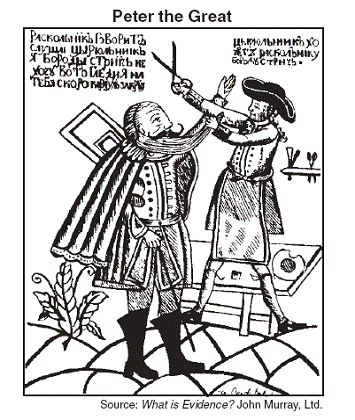
Base your answer to question 5 on the cartoon
below and on your knowledge of social studies.
5 The cartoon is commenting on the efforts of
Peter the Great to force the Russian nobility to
(1) conform to Asian social values
(2) adopt Western culture
(3) prepare for military battle
(4) bow to pressures from the Ottoman Empire
6. Which development in Russian history led to the other three?
(1) Orthodox Christianity was adopted in Russia.
(2) Trade developed along rivers linking Russia and the Byzantine Empire.
(3) The Cyrillic alphabet became the basis of Russian written language.
(4) Russian rulers took the title of czar, or caesar.
8 During the 1400s, the cities of Venice, Constantinople, and Canton achieved prominence because their
(1) locations were favorable for trade
(2) pleasant climates led to an increase in population
(3) democratic governments attracted trade
(4) military power led to industrialization
9. “. . . and in the actions of men, and especially of
princes, . . . the end justifies the means.”
Which philosopher most likely wrote this statement?
1 Baron de Montesquieu
2 Niccolò Machiavelli
3 Voltaire
4 John Locke
Base your answers to questions 10 and 11 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of social studies.
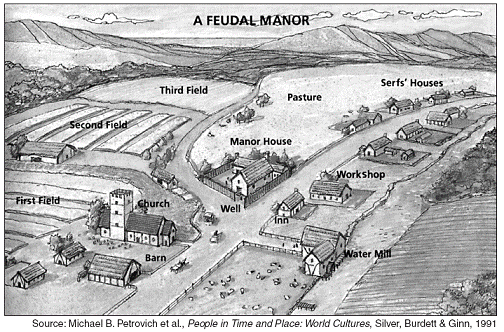
11 Most economic activities on this feudal manor were related to
(a) guilds
(b) banking
(c) industry
(d) agriculture
12 Which economic concept can be inferred from this diagram?
(a) self-sufficiency
(b) trade embargo
(c) inflation
(d) competition
13 The Magna Carta, the Petition of Right, and the English Bill of Rights were created to
(1) limit the power of English monarchs
(2) establish laws protecting the rights of Protestants
(3) organize England’s colonial empire
(4) abolish the role of Parliament
14 The theory justifying a monarch’s rule by God’s authority is called
(1) laissez faire (3) predestination
(2) totalitarianism (4) divine right
15. One similarity in the rule of Peter the Great, Elizabeth I, and Louis XIV is that each leader
(1) shared power with a legislature
(2) practiced religious toleration
(3) expanded his territory
(4) decreased the amount of taxes collected
16. In 1066, William (the Conqueror) of Normandy conquered ____.
a) England b) France c) Japan d) the Holy Land
17. The Wars of the Roses were struggles between
(a) noble families for the English throne
(b) noble families for the French throne
(c) England and Spain for overseas colonies
(d) Prussia and Austria over Silesia.
18. Laws based on decisions of judges is called ____.
a) totalitarianism b) common law c) marshal law d) judge’s law
19. The fourteen year old woman that led France to victory over the English is the Hundred Years
War was ___.
a) Elizabeth I b) Joan of Arc c) Felicia the Round d) Louisa XI
20. A government controlled by a king or queen is called a(n) _____.
a) dictatorship b) republic c) monarchy d) jazzercise
21. The ruling legislature in England is _____.
a) Congress b) Senate c) Parliament d) House of Governors
22. The document that took power from the English king and established an English representative government was the ____.
a) Hammurabi’s Code b) Divine Right c) Counter Refomration d) Magna Carta
23. The present monarch of England is _____.
a) Elizabeth I b) Elizabeth II c) Henry VIII d) Richard III
24. The theory that the monarch is a representative of God is called ____
a) predestination b) Divine Right c) common law d) Magna Carta
25. The war between England and France where the French took back their country was ___.
a) Thirty Years War b) Hundred Years War c) Six day war d) War of the Roses
7. The great aim of Louis XIV was to (1) preserve the balance of power in Europe (2) annex the German states (3) establish colonies throughout America (4) acquire territories up to France's natural boundaries.
8. The Asian invaders who ruled in Russia from the 13th to the 15th centuries were the (1) Mongols (2) Chinese (3) Turks (4) Huns.
9. At the end of the 18th century, Poland was partitioned by Prussia, Russia, and (1) Austria (2) Belgium (3) France (4) Sweden.
10. Which royal family is correctly paired with the country it ruled? (1) Prussia—Hapsburgs (2) Spain—Tudors (3) Russia—Romanovs (4) England—Bourbons.
11. Not a legislative body was (1) the Cortes (2) the House of Lancaster (3) the Estates-General (4) Parliament.
12. Joseph II of Austria was an outstanding (1) military leader (2) enlightened despot (3) defender of the Catholic Church (4) author who wrote the Pragmatic Sanction.
13. Which contributed to the rise of national states in western Europe? (1) the rise of a feudal nobility (2) the need for protection from barbarian invasions (3) the acquiring of colonies in the New World (4) the growth of the middle class.
14. The middle class believed that a strong king would' (1) protect life and property (2) give the middle class the right to vote (3) maintain local tariffs (4) assure religious unity.
15. In 18th-century Europe autocratic rulers based their claim to rule on (1) the consent of the Church (2) the support of the nobility (3) the theory of divine right (4) the support of the middle class.
China, Japan, and India in the Middle Ages
1. In the Middle Ages Moslem peoples were attracted to India because (1) India was the birthplace of Mohammed (2) Hindu princes invited Moslem missionaries (3) the topography of northwest India was similar to that of Arabia (4) northwest India had much wealth.
2. Which regions were the centers of Moslem population in India? (1) Indus and Ganges (2) Ganges and Deccan (3) Deccan and Himalayas (4) Himalayas and Indus.
3. Many Moslem rulers accused the Hindus of idolatry because the Hindus (1) accepted caste (2) believed in reincarnation (3) considered the cow sacred (4) carved religious statues.
4. The Taj Mahal was a famous (1) Hindu temple (2) Hindu palace (3) Moslem tomb (4) Moslem victory arch.
5. The _____ are winds that blow, with considerable regularity, over India
a) kamikazes b) monsoons c) tornadoes d) rangoons
6. A religious leader of India whose teaching are practiced more widely in other parts of Asia is __.
a) Confucius b) Moses c) Jesus d) Buddha
7. The European nation that first reached India by sea and monopolized India's trade for many years was (1) Portugal (2) England (3) France (4) Holland.
8. A period of Chinese history that compared favorably with the Han Period in military power, economic prosperity, and cultural achievement was the (1) T'ang (2) Sung (3) Ming (4) Manchu.
9. Most similar to the 11th-century Sung economic reforms is today's United States law (1) establishing minimum wages (2) providing social security (3) authorizing the government to purchase agricultural surpluses (4) prohibiting false labeling.
10. At its greatest extent, the Mongol Empire stretched westward from the Pacific Ocean to (1) Persia (2) Sinkiang (3) European Russia (4) central Europe.
11. During the Mongol Era the civilization of China was (1) destroyed by the Mongols (2) opened to new ideas from the rest of Asia (3) tolerated by the Mongols but considered inferior (4) replaced by Indian culture.
12. The medieval Chinese (1) learned block printing from India (2) used gunpowder only for nonmilitary purposes (3) did not develop logical methods of experimentation and research (4) learned of the compass from the Arabs.
13. Zheng He was a ____.
a) Chinese emperor b) Chinese explorer c) Japanese priest d) Korean businessman
15. The geographic relationship of the Asian continent to Japan is similar to the relationship of Europe to (1) Spain (2) Britain (3) Denmark (4) the United States.
16. The mountains of Japan (1) provide great natural beauty (2) contain much iron ore (3) are a barrier against invasion (4) contain much fertile land.
17. By the 9th century A.D. the Japanese had (1) developed an inbred culture (2) borrowed heavily from China's culture (3) adopted Hinduism from India (4) driven Catholic missionaries from their country.
18. Feudal Europe's closest counterpart to the shogun of feudal Japan was the (1) mayor of the palace (2) pope (3) knight (4) king.
19. Japan's last, or Tokugawa, Shogunate (1) failed to maintain law and order (2) caused economic ruin (3) drove out Buddhist priests (4) delayed Japan's development as a modern nation.
20. Japanese suicide pilots in World War II were called "kamikaze" after a (1) Japanese military leader who invaded Korea (2) Shinto god (3) typhoon that helped destroy a Mongol invasion fleet (4) towering Japanese mountain.
21. Why did Japan isolate itself from Western civilization in the 17th century? (1) Few Japanese had converted to Catholicism. (2) The Japanese resented the poor quality of European goods. (3) The Japanese discovered their own deposits of iron ore. (4) The Japanese feared that European missionary and trade activities would lead to military conquest.
22. Which was not an aspect of Japanese culture? (1) a complex system of writing (2) equality of all classes (3) Shinto emphasis on nature worship (4) respect of good manners and personal dignity.
23. Shintoism did not (1) originate as nature worship (2) consider the emperor a descendant of the gods (3) emphasize concern for the poor and the unfortunate (4) encourage Japanese nationalism.
1. The prosperity of China under the Ming dynasty was determined by
a) defeating the Manchu invaders
b) constructing the Great Wall along the northern frontier
c) expanding trade by sea with nations of Asia and Africa
d) establishing colonies in Korea and Japan
2. The Mongol Empire was started by
a) Kublai Khan b) Genghis Khan c) Aga Khan d) Chaka Khan
3. The dynasty that controlled China after the fall of the Mongol Empire was the ___ dynasty.
a) Han b) Sung c) Ming d) Yuan
4. Which major island of Japan has the most large cities in all of Japan?
a) Hokkaido b) Kyushu c) Shikoku d) Honshu
5. Which describes the land of Japan?
a) fertile farmland b) mountains c) dense forests d) arid desert
4 Zheng He contributed to the prosperity of China under the Ming dynasty by
(1) defeating the Manchu invaders
(2) constructing the Great Wall along the northern frontier
(3) expanding trade with nations of Asia and Africa
(4) establishing colonies in Korea and Japan
1. The Italian merchant that traveled to China in the 13th century and met Kublai Khan was ___.
a) Julius Caesar b) Christopher Columbus c) Marco Polo d) Luciano Pavarotti
2. The name of the dynasty founded by Kublai Khan in China was called the ___ dynasty.
a) Han b) Sung c) Ming d) Yuan
3. Which statement is best supported by the information on this map?
a) 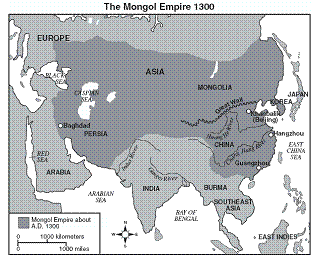 By 1300, the Mongol Empire had reached the Red Sea.
By 1300, the Mongol Empire had reached the Red Sea.
b) The Mongol Empire controlled India and Japan by 1300.
c) By 1300, most of Europe had been conquered by the Mongols.
d) The Mongol Empire controlled a large portion of Asia by 1300.
4. Which major island of Japan is the least populated?
a) Hokkaido b) Kyushu c) Shikoku d) Honshu
5. Which country is physically the closest to Japan?
a) China b) United States c) India d) France
Africa
The kingdom that developed around the time of ancient Egypt in the Upper part of the Nile was __.
a) Kush b) Axum c) Songhai d) Zimbabwe
A large part of Africa is ___.
a) desert b) rainforest c) savannah d) fertile farmland
The capital of the Kush empire was ____.
a) Cairo b) Meroe c) Timbuktu d) Capetown
The ancient African empire that is present day Ethiopia is ___.
a) Kush b) Axum c) Songhai d) Zimbabwe
Between A.D. 800 and 1600, the West African city of Timbuktu became prosperous with the trading of
(1) spices and silk
(3) gold and salt
(2) iron ore and coal
(4) rifles and diamonds
The first African empire in West Africa was ___. The name of the empire means gold.
a) Axum b) Ghana c) Songhai d) Mandingo
Which term best completes the partial outline below?
I. Rise of Civilizations of Ghana and Mali
A. ______________________
B. Spread of Islam
C. Development of centers of learning
(1) Use of gunpowder
(2) Trade of gold and salt
(3) Development of Hammurabi’s Code
(4) Distribution of the printing press
Mansa Musa was a(n)____.
a) rich ruler of the Mali empire
b) pharaoh of Egypt
c) Arab trader that settled in Zimbabwe
d) African traveler across the Mediterranean Sea
Ibn Battuta was a(n) ____.
a) rich ruler of Mali
b) Arab who wrote about the empire of Mali
c) Egyptian ruler
d) Trader in Zimbabwe
_____ was the most powerful inland state to export gold to the coastal cities of East Africa
a) Mali b) Zimbabwe c) Songhai d) Kush